Aluminum Extrusion in Vietnam
At ABC Vietnam, we specialize in transforming aluminum billets into precisely shaped profiles through the art and science of extrusion. As a leading aluminum extrusion factory in Vietnam, we produce all extruded products with certifications, ensuring our products meet the highest quality standards.
What is Aluminum Extrusion?
Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process that involves pushing aluminum through a die to produce parts with specific cross-sectional shapes. This method turns aluminum into strong light components that manufacturers can mold into intricate designs. As a result, many industries such as building, electronics, and transport prefer to use this technique.
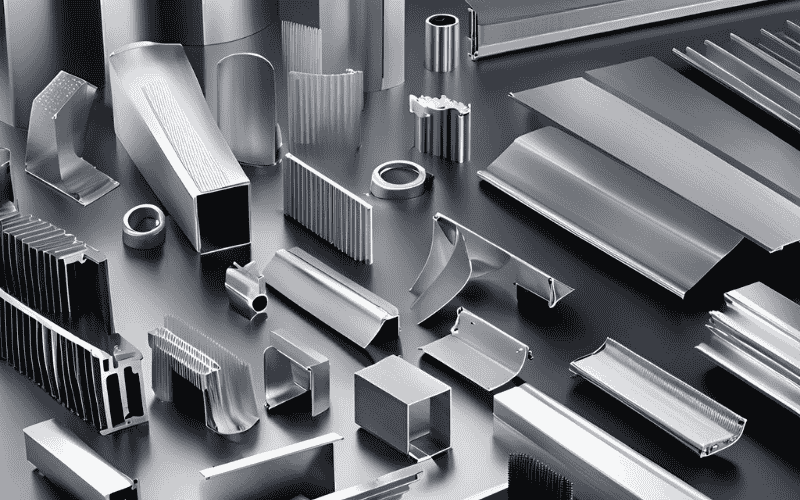
How Does the Aluminum Extrusion Process Work?
Understanding the aluminum extrusion process requires breaking it down into four key steps, each critical to the final product.
Step 1: Preparing the Aluminum Billet
The process begins with aluminum billets, which are solid cylindrical blocks of aluminum. These billets are heated to temperatures between 400°C and 500°C to make them malleable, allowing the material to be shaped without breaking.
- The choice of aluminum alloy affects the extruded product’s strength, corrosion resistance, and other properties.
- Proper heating ensures uniformity during extrusion.
Step 2: Die Design and Setup
A die is a custom-made tool that determines the shape of the extruded aluminum profile. Dies are carefully designed to meet specific design and performance criteria.
Step 3: The Extrusion Process
The heated aluminum billet is placed into the extrusion press. Using hydraulic pressure, the aluminum is pushed through the die, emerging on the other side in the desired shape.
- The extruded aluminum is immediately cooled to maintain its structural integrity.
- Once cooled, it is cut to the required length.
Step 4: Post-Extrusion Treatments
To enhance the material’s properties, post-extrusion treatments may be applied, such as:
- Anodizing: Improves corrosion resistance and enhances aesthetic appeal.
- Heat Treatment: Increases strength and durability.
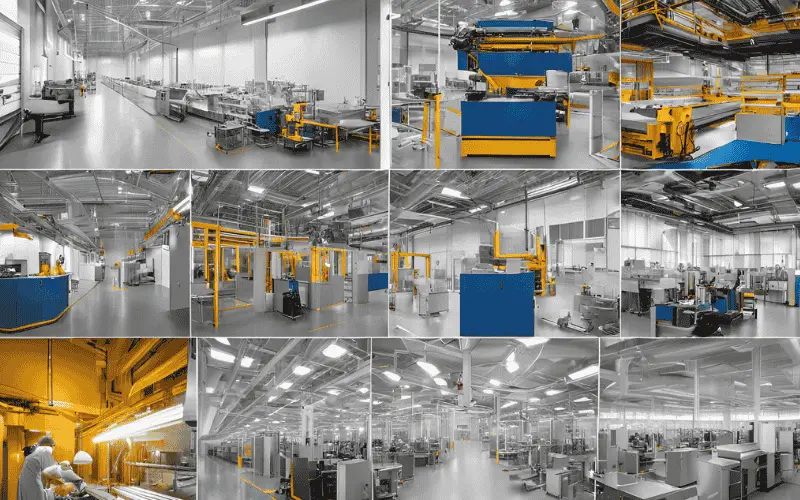

Post-processing of Aluminum Extrusion
Our state-of-the-art facility houses an array of post-processing technologies, enabling us to tailor aluminum extrusions to your exact needs:
- CNC machining
- Laser cutting
- Clinching
- Assembly
- Bending
- TIG welding
- Robot welding
- Laser Welding
After the die extrusion process, the sharp edges are removed from the parts and, if required, sawn to the right length. This is only done with mill-finished profiles.
Surface treatments we offer
We offer a range of secondary surface finishing processes to elevate the appearance, durability, and performance of your aluminum extrusions:
- Polishing
- Anodizing
- Chromating
- Sandblasting (glass beads, stainless steel beads, or aluminum grit)
- Powder coating
Key Factors in Aluminum Extrusion
Several factors influence the quality and properties of aluminum extrusions:
Aluminum Alloys
The choice of aluminum alloy significantly impacts the final product’s characteristics. Different alloys offer varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and formability.
| Alloy | Properties | Applications |
| 6061 | Medium strength, good corrosion resistance, weldable | Automotive parts, structural components, bicycle frames |
| 6063 | Good extrudability, corrosion resistance, suitable for anodizing | Architectural applications, window frames, door frames |
| 7075 | High strength, good fatigue resistance | Aerospace components, high-performance sporting goods |
Die Design and Its Impact
The die design is critical in determining the final shape and complexity of the extruded profile. Sophisticated die designs allow for intricate geometries and hollow sections. The precision and quality of the die directly affect the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the extrusion.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes further enhance the mechanical properties of aluminum extrusions. Common heat treatments include:
| Heat Treatment | Effect |
| T4 | Solution heat-treated and naturally aged |
| T6 | Solution heat-treated and artificially aged |
These treatments improve strength, hardness, and stress resistance, tailoring the material for specific applications.
Direct vs Indirect Extrusion
There are two main methods of aluminum extrusion: direct and indirect. The table below summarizes their key differences:
| Feature | Direct Extrusion | Indirect Extrusion |
| Billet Movement | Billet moves relative to the container | The billet remains stationary, and the die moves |
| Friction | Higher friction between the billet and the container | Lower friction |
| Pressure Required | Higher pressure | Lower pressure |
| Surface Finish | Can have surface imperfections due to friction | Better surface finish |
| Suitable Alloys | Soft alloys | Hard alloys |
Applications Across Industries
Our certified aluminum extrusions cater to diverse industries:
- Food-Related Devices: Hygienic and corrosion-resistant parts for food processing and packaging equipment
- Automotive: Lightweight and strong components for enhanced fuel efficiency and performance
- Medical: Precision parts for medical devices and equipment, meeting stringent hygiene standards
- Machinery & Devices: Frames, enclosures, and structural elements for industrial applications
- Electronics: Heat sinks, housings, and components for optimal thermal management
- Renewable Energy: Mounting systems and structural elements for solar panels and wind turbines
- EV Charging Solutions: Durable and safe components for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
Choose Us for Your Automobile and Motorbike Products
Whether you’re a seasoned automotive manufacturer or an emerging player, we can tailor our services to your needs. From prototyping to mass production, we guide you through every step of the manufacturing journey, ensuring your vision is realized with precision and efficiency. Contact us today to explore how we can fuel your automotive ambitions
Aluminum extrusion assembled products manufactured in Vietnam
Heat
exchanger
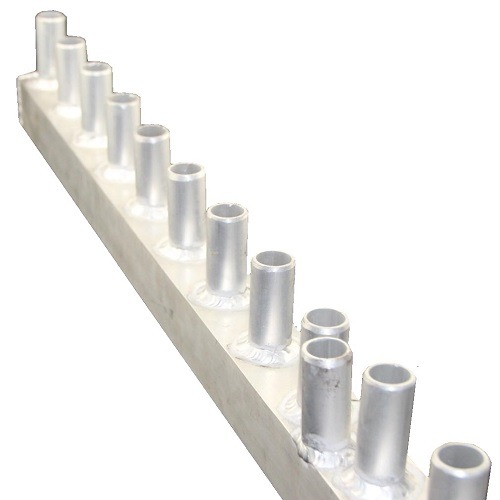

Used in a wide range of industries such as HVAC, power plants, chemical processing, and refrigeration, to transfer heat between fluids
Solar panel mounting
mid clamp
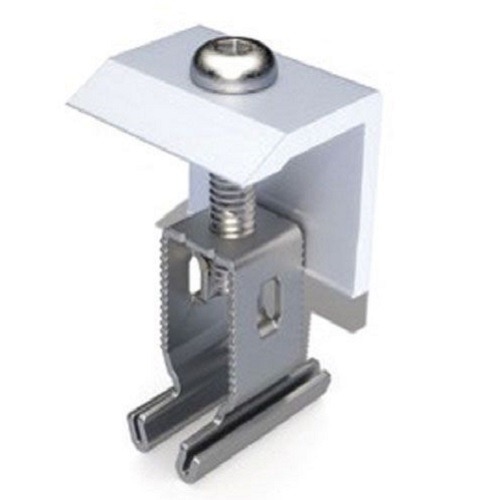

A solar panel mounting mid clamp securely attaches panels to rails, ensuring stability and proper alignment during installation
Adjustable corner
brackets
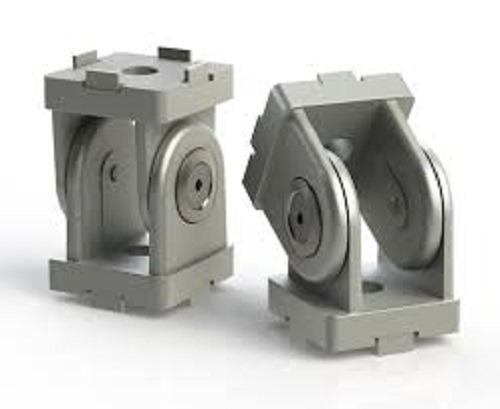

Securely attach and support solar panels to mounting structures, allowing for flexible installation by adjusting angles and positioning
Adjustable mounting
plate
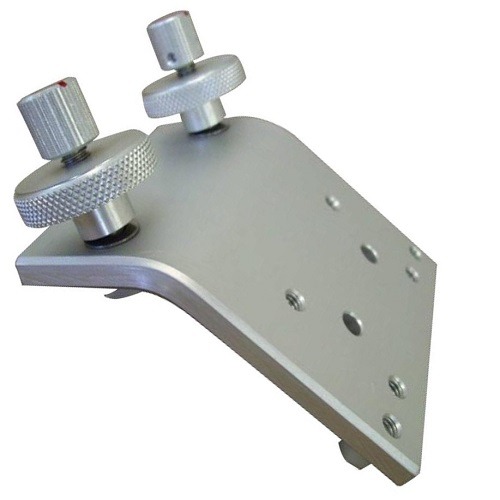

Secure solar panels to mounting structures while allowing for angle and position adjustments, providing flexibility in optimizing panel orientation for maximum efficiency
Heat
sink
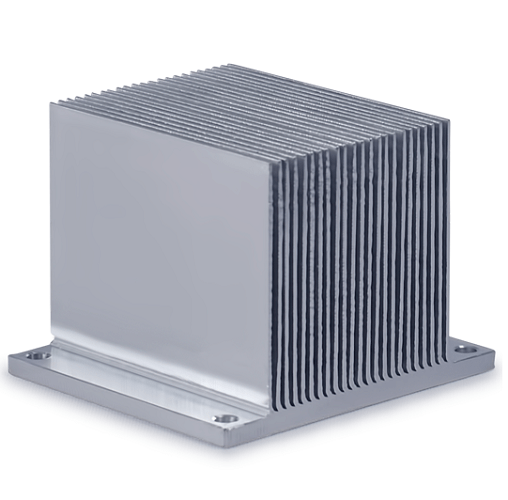
Dissipate heat away from electronic components, preventing overheating, and improve devices’ efficiency and longevity by maintaining optimal temperature levels
Liquid cooling
radiator
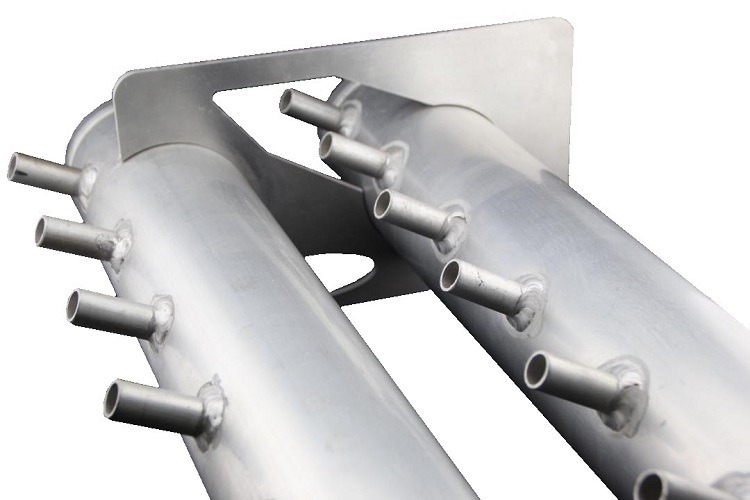

Dissipate heat from a liquid coolant, cooling down components like computer processors or car engines. It improves temperature control and prevents overheating for efficient performance
